BMI Calculator - Find Your Body Mass Index
Result:
Welcome to our comprehensive Body Mass Index (BMI) calculator. This advanced tool calculates your BMI using the standard formula and provides detailed health insights, weight status classification, and personalized recommendations. Our BMI calculator not only shows your current BMI but also helps you understand what it means for your health.
What is BMI?
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a standardized measure that uses your height and weight to determine if you're in a healthy weight range. It's widely used by healthcare professionals as a screening tool for weight-related health risks.
On this comprehensive page, you'll discover everything about Body Mass Index including detailed calculations, BMI categories, health implications, limitations, and practical applications for maintaining optimal health.
Understanding Body Mass Index (BMI)
BMI stands for Body Mass Index, a numerical measure that evaluates whether your weight is appropriate for your height. Developed in the 1830s by Belgian mathematician Adolphe Quetelet, BMI provides a standardized method for assessing weight status across populations.
BMI Purpose
Primary Use: Population health screening
Benefits: Quick, cost-effective assessment
Application: Medical and fitness contexts
Scope: Adults aged 18-65 primarily
Health Significance
Risk Assessment: Weight-related health issues
Conditions: Heart disease, diabetes, hypertension
Prevention: Early intervention guidance
Monitoring: Weight management progress
BMI serves as an important screening tool because it can indicate whether someone's weight may increase their risk of developing various health conditions. Research has consistently shown correlations between BMI ranges and health outcomes, making it valuable for both individual assessment and public health policy.
However, it's crucial to understand that BMI alone doesn't tell the complete health story. We'll explore its limitations and discuss complementary health assessments throughout this guide.
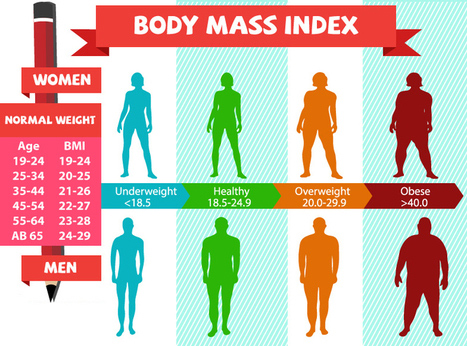
How to Calculate BMI - Complete Guide
BMI calculation uses a standardized mathematical formula that relates your weight to your height squared. There are two main formulas depending on your measurement system:
Imperial Formula (US)
Formula:
BMI = (weight in pounds ÷ height in inches²) × 703
Example: 5'7" (67 inches), 140 lbs
BMI = (140 ÷ 67²) × 703
BMI = (140 ÷ 4,489) × 703
BMI = 0.0312 × 703 = 21.9
Metric Formula (International)
Formula:
BMI = weight in kg ÷ (height in meters)²
Example: 1.70m, 64kg
BMI = 64 ÷ (1.70)²
BMI = 64 ÷ 2.89
BMI = 22.1
Step-by-Step BMI Calculation
Detailed Example: 5'5" (65 inches), 150 lbs
Step 1: Convert height to inches
5 feet 5 inches = (5 × 12) + 5 = 65 inches
Step 2: Square the height
65² = 65 × 65 = 4,225 inches²
Step 3: Apply the formula
BMI = (150 ÷ 4,225) × 703
BMI = 0.0355 × 703 = 24.9
Result: BMI of 24.9 (Normal weight range)
BMI Categories and Health Implications
The World Health Organization (WHO) and medical institutions worldwide use standardized BMI ranges to classify weight status. Each category carries different health implications and risk factors:
| BMI Range | Category | Health Risk | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| < 18.5 | Underweight | Moderate Risk | May indicate malnutrition, eating disorders, or underlying health conditions |
| 18.5 - 24.9 | Normal Weight | Lowest Risk | Associated with optimal health outcomes and longevity |
| 25.0 - 29.9 | Overweight | Moderate Risk | Increased risk for cardiovascular disease and diabetes |
| 30.0 - 34.9 | Obese Class I | High Risk | Significantly increased health risks |
| 35.0 - 39.9 | Obese Class II | Very High Risk | Severely increased health complications |
| ≥ 40.0 | Obese Class III | Extremely High Risk | Morbid obesity requiring immediate intervention |
Detailed Health Risk Analysis
Underweight Risks
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Weakened immune system
- Fertility problems
- Osteoporosis risk
- Delayed wound healing
- Mental health concerns
Normal Weight Benefits
- Optimal cardiovascular health
- Lower diabetes risk
- Better mobility and energy
- Improved sleep quality
- Enhanced self-esteem
- Longer life expectancy
Overweight Risks
- High blood pressure
- Type 2 diabetes
- Heart disease
- Stroke risk
- Sleep apnea
- Joint problems
Obesity Complications
- Severe cardiovascular disease
- Type 2 diabetes complications
- Certain cancers
- Fatty liver disease
- Respiratory problems
- Mental health issues
Using Our BMI Calculator
To make calculating your BMI easy, we've developed a simple online BMI calculator tool. Just input your height and weight:
The calculator will instantly compute your BMI and display which category you fall into based on the standard BMI ranges. It will also tell you how much weight you need to lose to reach your ideal BMI.
Knowing where your BMI lands can motivate you to make any needed lifestyle changes to reach a healthier weight for your body.
BMI Limitations and Alternative Assessments
While BMI is widely used and valuable for population health screening, understanding its limitations is crucial for accurate health assessment. BMI doesn't differentiate between muscle, bone, and fat mass, which can lead to misclassification in certain individuals.
Key Limitations of BMI
⚠️ BMI Doesn't Account For
- Muscle mass: Athletes may have high BMI but low body fat
- Bone density: Affects overall weight without indicating health risk
- Fat distribution: Visceral vs. subcutaneous fat differences
- Age factors: Muscle loss and body composition changes
- Gender differences: Men vs. women body composition variations
- Ethnicity: Different populations have varying health risk thresholds
✅ Complementary Assessments
- Body fat percentage: More accurate body composition measure
- Waist circumference: Indicates abdominal obesity risk
- Waist-to-hip ratio: Fat distribution assessment
- DEXA scan: Precise body composition analysis
- Bioelectrical impedance: Estimates body fat percentage
- Clinical evaluation: Complete health assessment
When BMI May Be Inaccurate
Special Populations
BMI may not accurately reflect health status for:
- Athletes and bodybuilders: High muscle mass increases BMI without health risk
- Elderly individuals: Age-related muscle loss affects BMI interpretation
- Growing children and teens: Require age and sex-specific BMI percentiles
- Pregnant women: Weight gain is expected and healthy
- Certain ethnic groups: May have different optimal BMI ranges
Enhanced Health Assessment Approach
For the most comprehensive health evaluation, healthcare providers combine BMI with additional measurements:
Comprehensive Health Screen Components
Physical Measurements
- BMI calculation
- Waist circumference
- Hip circumference
- Body fat percentage
Clinical Tests
- Blood pressure
- Cholesterol levels
- Blood sugar
- Thyroid function
Lifestyle Assessment
- Diet quality
- Physical activity level
- Sleep patterns
- Stress management

Body BMI Chart - Body Mass Index Chart
| Height (m) | Weight (kg) | BMI | Weight Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.52 | 44 | 19.0 | Normal |
| 1.52 | 56 | 24.2 | Normal |
| 1.52 | 63 | 27.2 | Overweight |
| 1.63 | 52 | 19.6 | Normal |
| 1.63 | 65 | 24.5 | Normal |
| 1.63 | 77 | 29.0 | Overweight |
| 1.73 | 60 | 20.0 | Normal |
| 1.73 | 75 | 25.0 | Overweight |
| 1.73 | 89 | 29.7 | Overweight |
| 1.83 | 67 | 20.0 | Normal |
| 1.83 | 83 | 24.8 | Normal |
| 1.83 | 100 | 29.8 | Overweight |
BMI and Weight Management Strategies
Achieving and Maintaining Healthy BMI
Whether you need to gain, lose, or maintain your current weight, sustainable lifestyle changes are key to reaching and maintaining a healthy BMI:
Weight Loss Strategies (BMI > 24.9)
- Caloric deficit: Consume fewer calories than you burn
- Portion control: Use smaller plates and measure servings
- Nutrient-dense foods: Focus on vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains
- Regular exercise: Combine cardio and strength training
- Hydration: Drink water before meals
- Sleep quality: Aim for 7-9 hours per night
Weight Gain Strategies (BMI < 18.5)
- Caloric surplus: Consume more calories than you burn
- Frequent meals: Eat 5-6 smaller meals throughout the day
- Healthy fats: Include nuts, avocados, olive oil
- Protein intake: Build muscle with adequate protein
- Strength training: Build lean muscle mass
- Medical consultation: Rule out underlying conditions
Setting Realistic Weight Goals
Safe Weight Change Guidelines
Healthy Weight Loss
1-2 lbs/week
Sustainable and safe rate
Healthy Weight Gain
0.5-1 lb/week
Focus on muscle, not fat
Weight Maintenance
±2 lbs
Normal fluctuation range
Comprehensive BMI FAQ
What is the ideal weight for a 5'2" female?
For a female who is 5'2" (157 cm) tall, a weight between 102-135 lbs (46-61 kg) is generally considered an ideal, healthy weight range. This corresponds to a BMI of 18.5-24.9.
At 5'2":
- A weight below 102 lbs would be underweight (BMI < 18.5)
- A weight of 102-135 lbs is a normal, healthy weight
- A weight of 136-164 lbs is overweight (BMI 25-29.9)
- A weight above 164 lbs is obese (BMI ≥ 30)
However, factors like body composition, muscle mass, frame size, and age can influence what weight is truly ideal for an individual 5'2" female. BMI is just one screening tool.
What is the ideal weight for a 5'10" male?
For a male who is 5'10" (178 cm) tall, a weight between 132-178 lbs (60-81 kg) is typically considered an ideal, healthy weight range with a BMI of 18.5-24.9.
At 5'10":
- A weight below 132 lbs would be underweight
- A weight of 132-178 lbs is a normal, healthy weight
- A weight of 179-214 lbs is overweight
- A weight above 214 lbs is obese
Highly muscular males at 5'10" may have a higher healthy weight due to increased muscle mass. BMI could underestimate their optimal weight.
What is the average weight for a 5'5" female?
For females of average build who are 5'5" (165 cm) tall, the average weight tends to fall between 125-160 lbs (57-73 kg), with higher weights for more muscular individuals.
At 5'5", the BMI ranges would be:
- Underweight: Below 117 lbs
- Normal Weight: 117-152 lbs
- Overweight: 153-185 lbs
- Obese: Above 185 lbs
However, the average or ideal weight can vary considerably based on body composition, frame size, and other factors.
What is considered a healthy weight for a 5'4" woman?
For a woman who is 5'4" (163 cm) tall, a healthy weight range would typically be between 110-144 lbs (50-65 kg), corresponding to a BMI of 18.5-24.9.
The BMI weight categories for a 5'4" woman are:
- Underweight: Below 110 lbs
- Normal Weight: 110-144 lbs
- Overweight: 145-175 lbs
- Obese: Above 175 lbs
As with other heights, highly active or muscular women of the same height may have a higher healthy weight due to increased muscle mass.
What is the formula to calculate BMI?
The formula to calculate BMI (Body Mass Index) is:
BMI = weight (kg) / [height (m)]2
Where:
- weight is measured in kilograms (kg)
- height is measured in meters (m)
For example, a person weighing 70 kg with a height of 1.7 m would have:
BMI = 70 kg / (1.7 m)2
= 70 kg / 2.89 m2
= 24.2
This value of 24.2 would fall into the normal/healthy BMI range of 18.5-24.9.
Tips for Success with BMI Management
Track Progress
Monitor BMI trends over time rather than focusing on single measurements. Use additional metrics like waist circumference.
Consult Professionals
Work with healthcare providers, registered dietitians, and fitness professionals for personalized guidance.
Holistic Approach
Focus on overall health, including mental well-being, not just BMI numbers. Sustainable lifestyle changes are key.
Key Takeaways
- BMI is a useful screening tool but has important limitations
- Normal BMI range (18.5-24.9) is associated with lowest health risks
- Body composition and lifestyle factors are equally important
- Sustainable diet and exercise habits matter more than BMI alone
- Individual assessment should consider multiple health factors
- Professional guidance enhances weight management success
Conclusion
BMI serves as an excellent starting point for assessing weight status and potential health risks. While it has limitations, when used appropriately alongside other health indicators, BMI provides valuable insights for maintaining optimal health.
Remember that true health encompasses much more than a single number. A comprehensive approach including nutritious eating, regular physical activity, adequate sleep, stress management, and preventive healthcare creates the foundation for long-term wellness.
Whether your BMI suggests you need to gain, lose, or maintain weight, focus on sustainable lifestyle changes that you can maintain long-term. Small, consistent improvements in diet and exercise habits often yield better results than drastic short-term measures.
Start Your Health Journey Today
Use our BMI calculator above to determine your current weight status and take the first step toward optimal health.
Find Calculator
Popular Calculators
Other Calculators
